
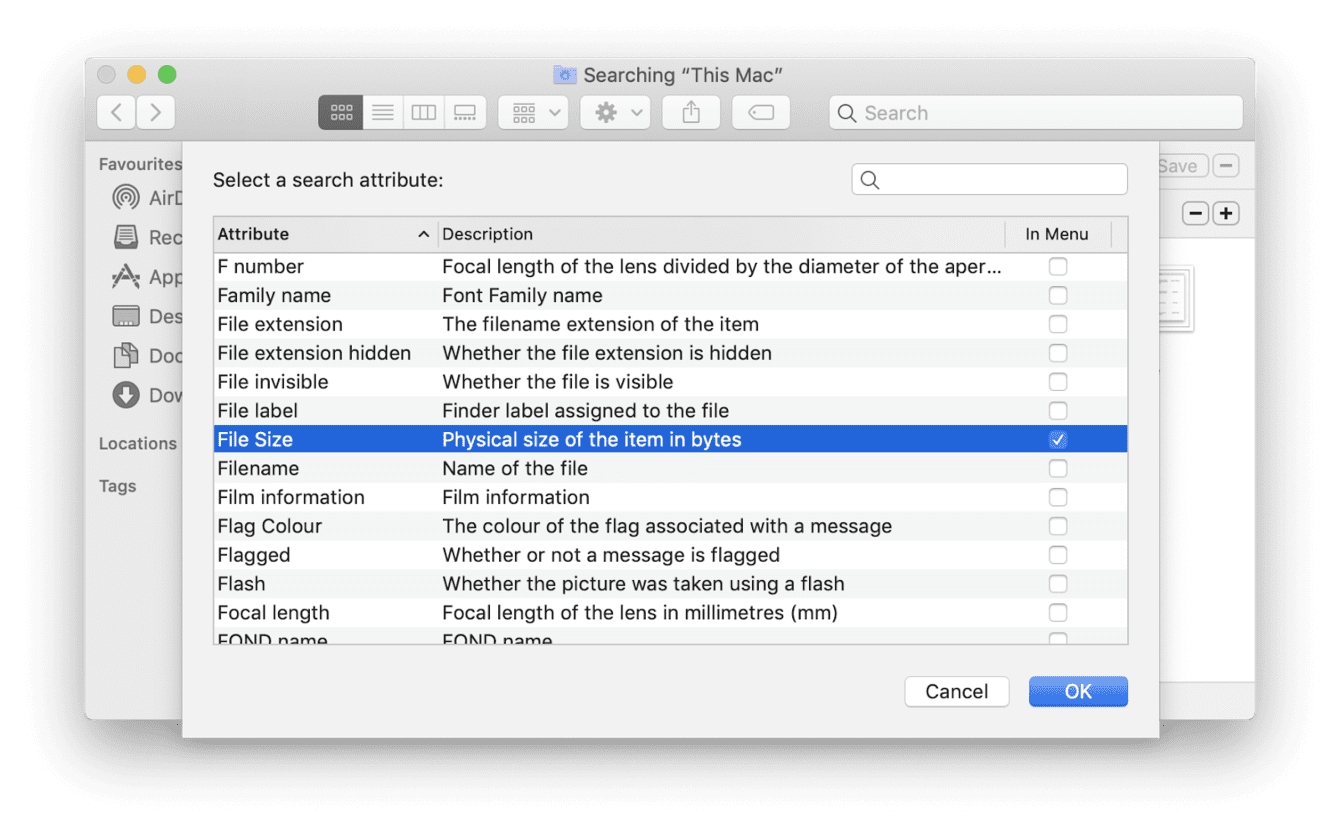
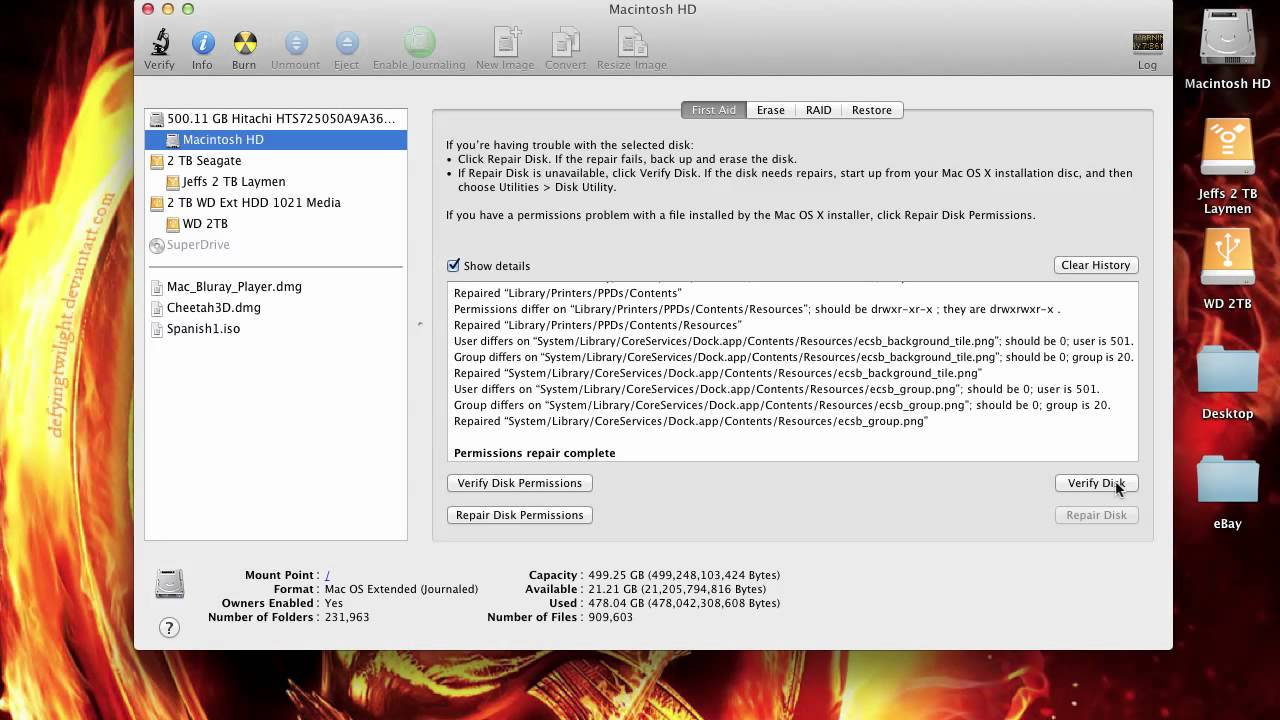
If you can't see this button, click Erase instead. Format: APFS or Mac OS Extended (Journaled), as recommended by Disk Utility.Click the Erase button in the toolbar, then enter the requested details:.Select Macintosh HD in the sidebar of Disk Utility.From the utilities window, select Disk Utility and click Continue.If asked, select a user you know the password for and enter their administrator password.Start up from macOS Recovery: turn on your Mac, then press and hold Command (⌘) and R immediately until you see an Apple logo or other image.Press the Enter key and your external drive will be erased completely.Next, type: diskutil eraseDisk JHFS+ (diskname diskidentifier).Now you’ll see a list of disks there, target yours through the disk identifier.Open it and enter this line: diskutil list.You can also try the Terminal app, though it’s a command-line tool that requires you to be a bit geeky. If for any reason Disk Utility fails to wipe your drive. Wipe External Hard Drive on Mac via Terminal (Command Line) It’s because SSDs don’t have to go through this process due to the way it manages files. Note: If your drive is an SSD, you won’t be able to click “Security Options” as this option will be grayed out. Here you can specify how securely you want to wipe the drive, move to Most Secure if you are paranoid because this option overwrites more times to the disk space, though the process tends to be slower.
Next, click the Security Options button at the bottom.Choose a file system to which you want to format your external drive.Select the disk or volume in the list on the left panel.Click on the Erase tab (next to “First Aid”).On your Mac, go to Applications > Utilities >Disk Utility.Then follow the step by step tutorial below: Make sure the device can be detected by the machine. First off, connect your external hard drive to your Mac.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
